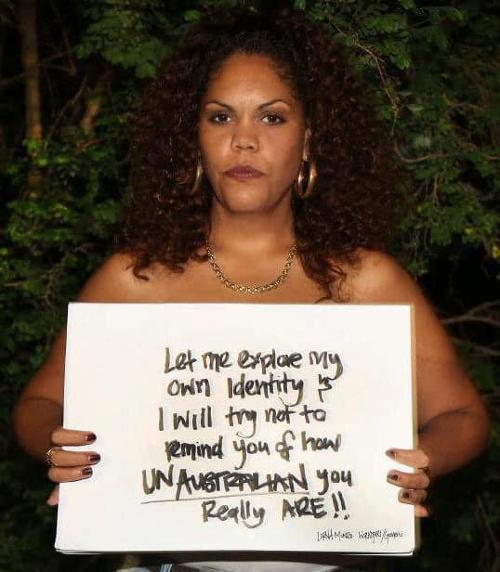Search
You searched for contributors, issues and articles tagged with Sovereignty ...
Contributors
Issues



Articles

My formal arts education began in a strange place: the Elisabeth Murdoch building at the University of Melbourne where I took an art history elective. Built in 1885 by Joseph Reed, the Gothic architecture reinforced the rigid authority of the colony. Glaringly elitist, it resembled both church and orphanage. It was full of confusing hallways, which remained impossible to navigate. Inside its constructed edifice, middle-aged white men in paisley shirts lectured, with exotic hand gestures, on First Nation artists (when they were spoken of at all). And white women in the faculty asserted a self-righteous paternalism that was far worse.
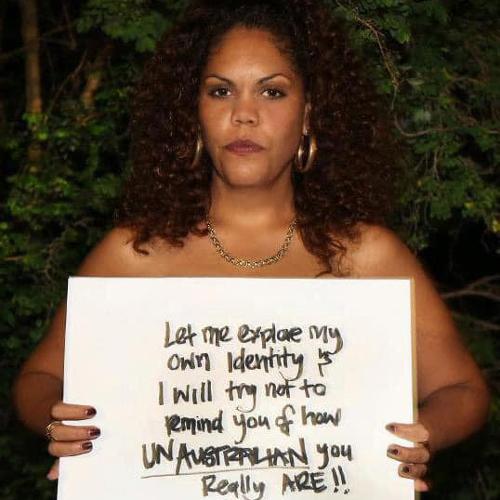
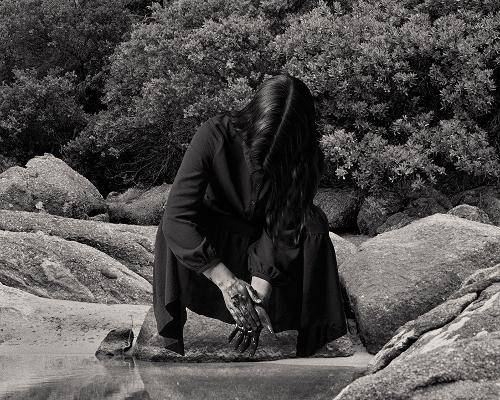
I paint my face as my mother’s mothers have done before me
In this new ritual sitting on my bedroom floor
We name each pigment after revolutionaries
Because I am my mother’s daughter

As people walk down that little wharf towards the canoe, I hope they remember how it was back in the day and how our old ancestors used to live and survive. And I want them to think back and imagine if they can, the women out in the canoes, and what it would have looked like and how beautiful it would have looked like with the fires going and we must not forget them, our ancestors. They were some special people. Because all the thousands of years they lived here says it all. It just says it all, how powerful and strong they were. And survivors… still survivors today.
Phyllis Stewart

A couple of years ago I quipped to my friend Alec Coles, who had recently taken up the position of CEO at the West Australian Museum, that the spirit of terra nullius lurks beneath the floorboards of every museum and art gallery in Australia. Apparently, he has dined out on this slightly parsimonious comment once or twice since. Alec likes to raise the stakes in discussions with his colleagues about the responsibilities that history demands of them as leaders of major collecting institutions—each with its own problematic legacy in terms of respecting and representing Indigenous culture.

Keynote address presented on 17 April 2015 in Perth as part of the annual Revealed program supporting emerging Aboriginal artists from Western Australia.
As Indigenous people of this nation we are a sovereign people, standing strong in our culture and remaining true to our heritage. We stand strong in our art; we stand strong in our culture and we stand strong on our country. Our ancestors, communities and families have welcomed many non-Indigenous peoples into this country, and today we see the continuity of our shared culture, history and traditions. I see Aboriginal art and culture at the very forefront of Australian identity and celebrated in such a way that previous generations would not have imagined. Despite these remarkable achievements, we as Aboriginal people in this country have been continually bombarded by waves of dispossession, racism, marginalisation and genocide. I am both angered and frustrated that we continue to sustain the impact of colonisation on a daily basis some 226 years after invasion. We are not recognised as a sovereign people, we continue to be governed by a nation that does not recognise us as equals.
Words are like territories. Like invisible boundaries laid down in the vast forest of experience, they parcel up reality into sections which can be named, like addresses or the clan estates of Arnhem Land. To compare two languages can be like overlaying the maps of two different cultures. Just as Manilakarr clan lands, for example, are split between Kakadu National Park and Arnhem Land, the conceptual boundaries of words in two languages rarely align neatly.

Yolngu have always had art inside our rumbal (bodies) and our doturrk (hearts). What people make depends on their aims, skill and style. With mobile phones and video cameras we’re making a new kind of Yolngu art. But it still comes from inside. It still comes from Yolngu doturrk.

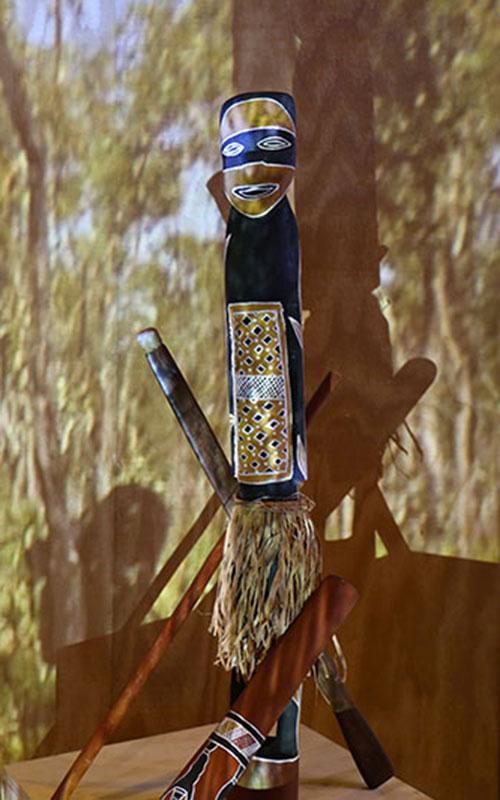
Yolngu people, the traditional Aboriginal owners of North East Arnhem Land, use the word mulka to describe a sacred, but public, ceremony. Mulka also means to protect and share things that are important to us – things that hold our identity, our culture, our connection to country and our past. When our people decided to bring together the films, photographs and audio recordings made in and about our community, the Mulka Project was born.

Beginning with batik printing at Ernabella in the APY Lands in the 1940s, hand-printed textiles in Indigenous art centres have become a rich and varied tradition. It has emerged as a significant art form in recent years, particularly for art centres in the Top End.
The Tiwi Islands has one of the longest traditions, where the Bima Wear women’s centre has been printing and designing since 1969, alongside Tiwi Design and the Pirlangimpi Women’s Centre. Tiwi textiles are known for their bright colours and bold designs, and are often worn by the local community.

Recent changes to the Western Australian Heritage Act undermine the connection between people and country, placing thousands of rock art galleries at risk. Since the introduction of the cattle industry to the Kimberley region during the early 20th century and the subsequent forced removal of Aboriginal people from their traditional homelands, negative impacts on Aboriginal communities have been well documented. The impact on country, when its people are removed, is equally dire according to Ngarinyin/Nyikina artist, cultural leader and land management professional Rona Charles: “You can’t take people, objects, Junba [song and dance] away from Country and think nothing will happen. Because water, plant, song, animal, people – they all depend on each other. People, for their identity and social wellbeing, and country for ecology.”
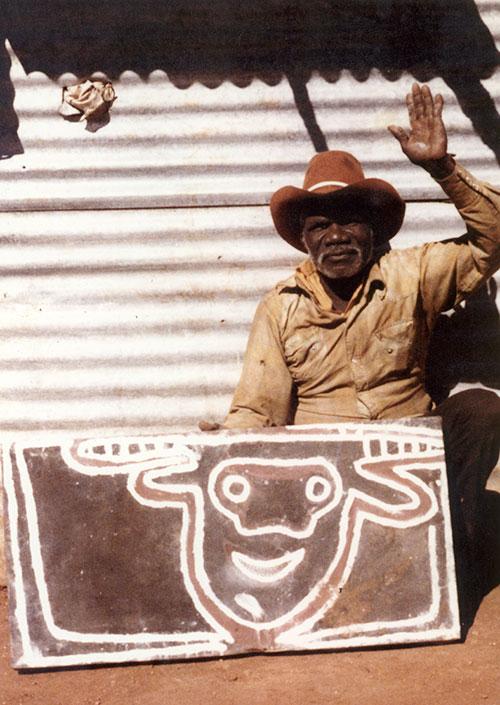

Painting at Warmun has long been linked with the desire of the old people to pass on Gija language to children. At the same time as the Goorirr-goorirr song and dance cycle was given to Rover Thomas by a spirit, Gija elders were requesting that the Ngalangangpum School teach their language. Paintings carried in the dance helped launch the local art movement and the singers and dancers were also the language teachers. They made objects as teaching aids that are now part of the Warmun Community Collection.

Under the guardians of the mission, Cornelia Tipuamantumirri grew up on Bathurst Island in the Tiwi Islands. She went to school under the old mission church and was given a slate and chalk. Salvation came in the form of the Catholic nuns. She lived in a dormitory with the other Tiwi girls. She was never allowed to speak her language or practice our culture.

I am a Garawa man. My country is in the southwest Gulf of Carpentaria. When I was young there was no whitefella schooling for us Aboriginal kids. My school was the bridle and the blanket, learning on the pastoral stations where my father worked. Our future was set as labourers on whitefella stations. This is the reason I don’t read and write. I’m not ashamed of this.
I was taught our law by my grandfathers, father, uncles and other senior kin from the southwest Gulf peoples: the Mara, Gudanji, Yanyuwa and Garawa. Knowledge came to me through ceremonies, hunting, fishing, gathering and travelling through our country with the old people. We sing the country.

This series explores living conditions in our community of Borroloola in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Northern Territory. I am a Yanyuwa/Garrwa woman. I call it “My country, no home” because we have a Country but no home, people are living in tin shacks, in matchbox-sized houses. Even traditional owners here don’t own houses. I wanted to take these photos to show the world how my people are living. The project is not to shame them.